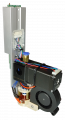
Difference between revisions of "Filament Heads"
| Line 61: | Line 61: | ||
# '''MK1-250''' Extruder for Standard Filament Videos: | # '''MK1-250''' Extruder for Standard Filament Videos: | ||
## [[File:Yt.png]] [https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yaCYFmoIESk Overview] | ## [[File:Yt.png]] [https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yaCYFmoIESk Overview] | ||
* [http://hyrel3d.net/downloads/Manuals/Data_MK1-250.pdf Data Sheet for the MK1-250 Head] | |||
## [[File:Yt.png]] [https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=v2ifSlZ0qEw Loading and Printing] | ## [[File:Yt.png]] [https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=v2ifSlZ0qEw Loading and Printing] | ||
# '''MK2-250''' Extruder for Flexible Filament Videos: | # '''MK2-250''' Extruder for Flexible Filament Videos: | ||
## [[File:Yt.png]] [https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SOGKeU3vLbs Overview] | ## [[File:Yt.png]] [https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SOGKeU3vLbs Overview] | ||
* [http://hyrel3d.net/downloads/Manuals/Data_MK2-250.pdf Data Sheet for the MK2-250 Head] | |||
## [[File:Yt.png]] [https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0dS3bC0BnRQ Loading and Printing] | ## [[File:Yt.png]] [https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0dS3bC0BnRQ Loading and Printing] | ||
# '''MK1-450''' Extruder for High-Temperature Filament Videos: | # '''MK1-450''' Extruder for High-Temperature Filament Videos: | ||
Revision as of 14:18, 15 February 2018
Hot Flow is our term for filament-based materials which are deposited at over 150°C, depending on the head.
Note that at present, our Hot Flow heads work with 1.75mm filament (actually, 1.6mm to 1.9mm), but not 3mm filament.
Materials for Hot Flow
The following materials can be printed from Hot Flow heads.
- ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene)
- Flame Retardant ABS
- ABS - PC Alloy
- Conductive ABS
- Smart ABS
- BendLay
- Flex 45
- HIPS (High-Impact PolyStyrene)
- LayBrick
- LayWoo-d3
- MoldLay
- Ninjaflex
- Nylon
- Taulman 618, 645, 910
- PC (PolyCarbnoate)
- PEI (PolyEtherImide) - AKA Ultem
- PEEK (PolyEther Ether Ketone)
- PET (PolyEthylene Terephthalate)
- PETG PolyEthylene Terephthalate Glycol-modified)
- PLA (PolyLactic Acid)
- EcoFlex PLA
- Conductive PLA
- SS PLA (Stainless Steel infused)
- PlastInk_Rubber
- PP (PolyPropylene)
- PVA (PolyVinyl Alcohol)
- T-Glase
- Ultem
Heads for Hot Flow
Hot Flow is available through the following heads:
- General MK Series Videos:
- MK1-250 Extruder for Standard Filament Videos:
- MK2-250 Extruder for Flexible Filament Videos:
- MK1-450 Extruder for High-Temperature Filament Videos:
 Overview
Overview Loading and Printing
Loading and Printing
The following table compares the properties of the various Hot Flow heads, including which heads are recommended for which materials. The MK1 heads drive matieral from one side, with a spring-loaded bearing system to maintain pressure and positioning. The MK2 heads drive the material from both sides, and are designed for more flexible filaments.
| Head | Min Temp | Max Temp | Filament Type | Nozzle | Recommended For |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MK1-250 | 150°C | 250°C | Standard | .35mm, .50mm, .75mm, 1.0mm | ABS, HIPS, LayBrick, LayWood, Nylon, PC, PET, PETG, PETT, PLA, PP, PVA, T-Glase |
| MK2-250 | 150°C | 250°C | Flexible | .35mm, .50mm, .75mm, 1.0mm | BendLay, EcoFlex PLA, FilaFlex, Flex45, Ninjaflex, PlastInk Rubber |
| MK1-450 | 275°C | 450°C | Engineering | .50mm, .40mm, .30mm | PEEK, PEI (Ultem) |
Research Papers Citing Hyrel Hot Flow
- Fabrication and Properties of Novel Polymer-Metal Composites using Fused Deposition Modeling by the Mechanical Engineering Staff at Worcester Polytechnic Institute
- NANOSATC-BR2, 2 unit CUBESAT, Power Analysis, Solar Flux Prediction, Design and 3D Printing of the Flight Model from the UFSM & INPE’S NANOSATC-BR, CUBESAT Development Program by a team from the Federal University of Santa Maria (UFSM), Brasil.
- A Preliminary Study of Conductive Filaments Printed Via Fused Filament Fabrication by Smruti Ranjan Sahoo at Rochester Institute of Technology
- Tensile Mechanical Properties of Polypropylene Composites Fabricated by Material Extrusion, a reviewed paper of the Solid Freeform Fabrication Symposium 2017.
- Effect of Process Parameters and Shot Peening on Mechanical Behavior of ABS Parts Manufactured by Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF), a reviewed paper of the Solid Freeform Fabrication Symposium 2017.
- Hybrid Processes in Additive Manufacturing in the Journal of Manufacturing Science and Engineering of the American Society of Mechanical Engineers
- Effects of Material Properties on Warpage in Fused Deposition Modeling Parts in The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology
- Thermal and Mechanical Properties of 3D Printed Boron Nitride – ABS Composites, in Applied Composite Materials
- Review of Batteryless Wireless Sensors Using Additively Manufactured Microwave Resonators in Sensors, a Journal of the Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute
- Self-Actuating 3D Printed Packaging for Deployable Antennas, The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, Incorporated (IEEE)
- Dynamical Majorana edge modes in a broad class of topological mechanical systems by The New Jersey Institute of Technology
- A Low-Cost, Single Platform, Hybrid Manufacturing System for RF Passives, The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, Incorporated (IEEE)
- Button-Shaped RFID Tag Combining Three-Dimensional and Inkjet Printing Technologies, The IET Digital Library.
- Demonstration and Characterization of Fully 3D-printed RF Structures, The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, Incorporated (IEEE)
- Infill Dependent 3D-Printed Material Based on NinjaFlex Filament for Antenna Applications, The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, Incorporated (IEEE)
- A Novel Strain Sensor Based on 3D Printing Technology and 3D Antenna Design, The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, Incorporated (IEEE)
- A Novel 3-D Printed Loop Antenna Using Flexible NinjaFlex Material for Wearable and IoT Applications, The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, Incorporated (IEEE)
- RF Characterization of 3D Printed Flexible Materials - NinjaFlex Filaments, The European Microwave Association (EuMA)
- Nano-Material Based Flexible Radio Frequency Sensors for Wearable Health and Environment Monitoring: Designs and Prototypes Utilizing 3D/Inkjet Printing Technologies, A Dissertation Presented to The Academic Faculty of The School of Electrical and Computer Engineering at Georgia Tech
Settings for Hot Flow Heads
Non-Hydra units shipping through spring 2017 ship with Repetrel version 2.x. Hydra units, and other units shipping as of summer 2017 will have version 3.x, and should consult the version 3.x tables, below. All units should be upgraded to 3.x when it is available.
| Values for version 2.x will be inicated in this manner. |
|---|
| Values for version 3.x will be inicated in this manner. |
Some settings for the MK-Type heads (like temperature, prime/unprime values) will vary, depending on what material you are printing with. Nozzle diameter should accurately reflect what nozzle you have loaded (0.5mm is default) AND what path width you sliced for (recipe path or extrusion width should be nozzle diameter plus 10%). Having said that, here are our default shipping settings:
| Settings | MK1-250 | MK2-250 | MK1-450 (formerly -350 or -400) |
MK1-650* |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Material | ||||
| Type | (any) | (any) | (any) | (any) |
| Color | (any) | (any) | (any) | (any) |
| Nozzle | 0.500 | 0.500 | 0.500 | 0.500 |
| Layer | (any) | (any) | (any) | (any) |
| Temp Info | ||||
| Print Temp | 240 | 240 | 410 | 800 |
| Power Factor | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Minimum | (any) | (any) | (any) | (any) |
| Maximum | (any) | (any) | (any) | (any) |
| Overrides | ||||
| Pulses: v2.x | 0.78 | 0.78 | 0.78 | 0.78 |
| Pulses: v3.x | 78 | 78 | 78 | 78 |
| Feed Rate % | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Prime Please note that Prime values will vary greatly from those shown, depending on the flexibility of your material. | ||||
| Steps | 200 | 200 | 200 | 200 |
| Rate | 10,000 | 10,000 | 10,000 | 10,000 |
| Dwell Time (ms): v2.x | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 |
| Dwell Time (ms): v3.x | 35 | 35 | 35 | 35 |
| Before Tool Change | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Unprime Please note that Unprime values will vary greatly from those shown, depending on the flexibility of your material. | ||||
| Steps | 200 | 200 | 200 | 200 |
| Rate | 10,000 | 10,000 | 10,000 | 10,000 |
| Dwell Time (ms): v2.x | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 |
| Dwell Time (ms): v3.x | -35 | -35 | -35 | -35 |
| After Tool Change | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Offsets | ||||
| Clone Head | Off | Off | Off | Off |
| X | 0,000 | 0,000 | 0,000 | 0,000 |
| Y | 0,000 | 0,000 | 0,000 | 0,000 |
| Z | 0,000 | 0,000 | 0,000 | 0,000 |
| Head Info | ||||
| Model | 250 | 250 | 350 | 650 |
| RTD Type | 1 Meg | 1 Meg | 1 Meg | 1 Meg |
| Motor Current | High | High | High | High |
| Step Mode | Sixteenth | Sixteenth | Sixteenth | Sixteenth |
| Settings | MK1-250 | MK2-250 | MK1-450 (formerly -350 or -400) |
MK1-650* |
| *In development. | ||||
Changing Nozzles
How to disassemble the nozzle from the MK1 head:
- Carefully:
- Heat to the printing temperature of the material loaded.
- Move the manual lever to the left, retracting material until it is free of the hobbed shaft, then remove by hand.
- Turn off heat to the head and remove it from the yoke.
- With a 1/4" driver or wrench, remove the nozzle.
- Inspect the nozzle cavity for any stray material; if found, remove with tweezers, solvent, air pressure or other means.
How to reassemble the nozzle on an MK1 head:
- Carefully:
- Ensure your MK1 has no filament loaded.
- With a 1/4" driver or wrench, attach the nozzle.
- Use normal procedure for heating and loading filament.