Gcode
What is GCode?
Everything your Hyrel 3D Printer does is done by executing GCode, whether you are aware of it or not.
Every button you press on the screen sends a gcode to the printer.
When you start a job (by pressing "Print"), the settings from your head are sent to the printer (including flow and prime/unprime values); then the gcode file is sent, line by line, to the printer.
All parameters are persistent, so once they are set, they will remain in place unless or until you (or the file) sends a new, updated value (including setting to 0).
Please note that there are many flavors of gcode, and while most have the same (or very similar) G0-G100 and M0-M100, codes above 100 are largely nonstandard.
It is important to remember that different variable letters can have different meanings, depending on the G- or M- code being used - especially the T value.
The Table of Contents to the right lists the main categories of Gcodes.
Below is a table listing them in numerical order (click Expand to expand):
| Code | Supported | Brief Description |
|---|---|---|
| G0 | Yes | Rapid Move |
| G1 | Yes | Working Move |
| G2 | Yes | Clockwise Arc |
| G2.1 | Yes | Spiral CW Arc1 |
| G2.2 | Yes | Spiral CW Arc2 |
| G2.3 | Yes | 3-Space CW Spiral Arc |
| G3 | Yes | Counterclockwise Arc |
| [[#G3.1_Spiral_CCW_Arc1|G3.1]] | Yes | Spiral CCW Arc1 |
| G3.2 | Yes | Spiral CCW Arc2 |
| G3.3 | Yes | 3-Space CCW Spiral Arc |
| G4 | Yes | Timed Pause |
| G10 | No | Absolute E |
| G11 | No | Relative E |
| G16 | Yes | Arc in Any Plane |
| G17 | Yes | Arc in XY Plane |
| G18 | Yes | Arc in XZ Plane |
| G19 | Yes | Arc in YZ Plane |
| G20 | Yes | Set Units to Inches |
| G21 | Yes | Set Units to Milimeters |
| G28 | Yes | Send X, Y to Physical Home |
| G53 | Yes | Clear Offsets |
| G54-59 | Yes | Set Offsets |
| G81 | G81 | Peck Drilling |
| G90 | Yes | Absolute Positioning |
| G91 | Yes | Relatative Positioning |
| G92 | Yes | Reset Coordinates |
| G93 | Yes | Reset Coordinates |
| M0 | Yes | Stop Until Resume |
| M3 | Yes | Spindle On CW |
| M4 | Yes | Spindle On CCW |
| M5 | Yes | Spindle Off |
| M6 | Yes | Declare Head Offsets |
| M7 | Yes | Aux 1 On (Mist) |
| M8 | Yes | Aux 2 On (Flood) |
| M9 | Yes | All Aux Off |
| M17 | Yes | Engage Motors |
| M18 | Yes | Disengage Motors |
| M30 | Yes | End of Program |
| M82 | Yes | Absolute E-Values |
| M83 | Yes | Relative E-Values |
| M84 | Yes | Disable Motors |
| M104 | Yes | Set Temp (Head) |
| M106 | Yes | Set Cooling / Etc. |
| M107 | Yes | Stop Cooling / Etc. |
| M109 | Yes | Wait for Temp (Head) |
| M116 | No | Pause for All Temps |
| M140 | Yes | Set Temp (Bed) |
| M141 | Yes | Set Temp (Chamber) |
| M190 | Yes | Wait for Temp (Bed) |
| M191 | Yes | Wait for Temp (Chamber) |
| M203 | Yes | Set G0 Speed |
| M221 | Yes | Set Flow Rate |
| M229 | Yes | Use E Values |
| M253 | Yes | Turn On Lathe (CW) |
| M254 | Yes | Turn On Lathe (CCW) |
| M255 | Yes | Turn Off Lathe |
| M619 | Yes | Map Aux Port |
| M620 | Yes | Enable Device |
| M621 | Yes | Set Laser Power |
| M623 | Yes | Duration Emit |
| M660 | Yes | Set Tool Offsets |
| M670 | Yes | Enable Y-arm Light |
| M671 | Yes | Activate Danger Light |
| M672 | Yes | Set Y-arm Light |
| M675 | Yes | Activate Response LEDs |
| M676 | Yes | Activate Recirc. Fan |
| M677 | Yes | Activate Buzzer |
| M678 | Yes | Activate Laser X-hair |
| M679 | Yes | Activate Vacuum |
| M684 | Yes | Activate Exhaust |
| M685 | Yes | Activate Air |
| M689 | Yes | Activate Ext. Head |
| M701 | Yes | Set Head Reporting |
| M702 | Yes | Establish Clone Squad |
| M703 | Yes | Add to Clone Squad |
| M704 | Yes | Remove from Clone Squad |
| M718 | Yes | Stop Logging to File |
| M719 | Yes | Start Logging to File |
| M721 | Yes | Set Unprime Values |
| M722 | Yes | Set Prime Values |
| M723 | Yes | Set Manual Flow |
| M728 | Yes | Set Motor Current Boost |
| M756 | Yes | Set Height for Flow |
| M772 | Yes | Reset All Metrics |
| M773 | Yes | Generate Basic Report |
| M783 | Yes | Tie Aux to Extrusion |
| M790 | Yes | New Layer Actions |
| M791 | Yes | Snap Image |
| M792 | Yes | Execute Action |
Understanding the T
A T Command changes which head has the focus of the motion controller and is executing the gcode. Each of our printers have at least four tool positions.
The use of T commands and variables changes greatly (for the better) with the jump to version 5 from the previous versions.
Please see T_v4 for the old way (v4 and earlier), where the nomenclature for T Commands and the T Variables were not the same.
Please see T_v5 for the new way (v5 and later), where the nomenclature for T Commands and the T Variables are the same.
We will use a T# in the descriptions below to avoid confusion; please find the correct designation for your version by following the links above.
Controlling Movement
| Controlling Movement | ||
|---|---|---|
| Code | Supported | Brief Description |
| G0 | Yes | Rapid Move |
| G1 | Yes | Working Move |
| G2 | Yes | Clockwise Arc |
| G2.1 | Yes | Spiral CW Arc1 |
| G2.2 | Yes | Spiral CW Arc2 |
| G2.3 | Yes | 3-Space CW Spiral Arc |
| G3 | Yes | Counterclockwise Arc |
| [[#G3.1_Spiral_CCW_Arc1|G3.1]] | Yes | Spiral CCW Arc1 |
| G3.2 | Yes | Spiral CCW Arc2 |
| G3.3 | Yes | 3-Space CCW Spiral Arc |
| G4 | Yes | Timed Pause |
| G16 | Yes | Arc in Any Plane |
| G17 | Yes | Arc in XY Plane |
| G18 | Yes | Arc in XZ Plane |
| G19 | Yes | Arc in YZ Plane |
| M0 | Yes | Stop Until Resume |
| M203 | Yes | Set G0 Speed |
G0 Rapid Move
G0 is a rapid positioning move. It is not a working move, meaning that your equipment will not be printing, milling, lasering, or doing any other active work during a G0 move. G0 is intended to move your tool to a new position, where the work will happen. Accordingly, G0 movement speeds are set in your configuration settings, rather than being specified in your gcode file.
Special note: a G0 command will take an F variable as a nonpersistent, one-time velocity setting.
Usage
G0 Xn Yn Zn An Bn Fn
Parameters
Xn is the new X position to move to Yn is the new Y position to move to Zn is the new Z position to move to An is the new A position to move to Bn is the new B position to move to Fn is the feed rate or travel speed to use. Only on G0 is it not persistent
Any values not stipulated remain unchanged.
Note: These positioning values can be absolute or relative to the last position; which depends on whether you are running on G90 absolute positioning or G91 relative positioning. Absolute is the default and should be used in the majority of cases.
Note: All Hyrel printers have built-in support for three axes. Hyrel model 16A and EHR printers may be expanded to five; an additional axis on each machine is reserved for E values.
Example
G0 X50 Y75 Z10
This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
- G0 (rapid (nonprinting) straight line move from the current location to)
- X50 (50mm in the X)
- Y75 (75mm in the Y)
- Z10 (10mm in the Z)
- (no change in A)
- (no change in B)
- (no change in F, use settings-specified feed rate)
G1 Working Move
G1 is a working move, during which you may be printing, milling, lasering, or doing other active work - provided an E (extrude) value is given. In native mode (if you don't add M229 E1 Dn, the value of Extrusion rate E will be ignored, but E will trigger a working or printing move. In E-value mode (by adding M229 E1 Dn, the slicer-determined E value will be used to control material flow. G1 moves are made at the rate indicated by the F (feed rate) value; if no F value is specified, the last F value set will be used. See M229 for more details.
Usage
G1 Xn Yn Zn An Bn Fn Sn
Parameters
Xn is the new X position to move to Yn is the new Y position to move to Zn is the new Z position to move to An is the new A position to move to Bn is the new B position to move to Hn is the stored head offset to apply (see M660 to store offsets) Fn is the feed rate or travel speed to use. Only on G0 is it not persistent Sn is a one-time (non-persistent) material flow rate multiplier (rarely used) applied to this move only
Any values not stipulated remain unchanged.
Note: These positioning values can be absolute or relative to the last position; which depends on whether you are running on G90 absolute positioning or G91 relative positioning. Absolute is the default and should be used in the majority of cases; there will be problems with an entire model sliced in relative mode. Relative is intended for special operations like drilling holes.
Note: All Hyrel printers have built-in support for three axes. Hyrel model 16A and EHR printers may be expanded to five; an additional axis on each machine is reserved for E values.
Example
G1 X50 Y75 E1 F1800 H2
This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
- G1 (working speed straight line move from the current location to)
- X50 (50mm in the X)
- Y75 (75mm in the Y)
- (no change in A)
- (no change in B)
- E1 (while extruding)
- F1800 (moving at 1800mm/min)
- H2 (invoking offsets stored in register H2)
- (no temporary scaling)
G2 Clockwise Arc
A G2 move specifies a clockwise arc (or complete circle) from the current position to position (X,Y,Z)curr by following an arc about the center point (Xcurr+I, Ycurr+J).
Usage
G2 Xn Yn Zn In Jn Fn En Sn
Parameters
Xn is the new X position to move to Yn is the new Y position to move to Zn is the new Z position to end at (optional and usually not stipulated) In is the relative distance from the current X position to the center position about which to arc (default 0) Jn is the relative distance from the current Y position to the center position about which to arc (default 0) Fn is the Feed rate (travel speed) at which to execute this move. En indicates a working or printing move Sn dictates how many segments are used to create the arc (or circle); 0.33333 mm is the default value S values less than 3.0 dictate the length in mm of each segment for this element S values of 3.0 or more dictate how many total segments comprise this element - only allowed on complete circles of 360°
Any values not stipulated remain unchanged. We will print this element with our native Hyrel flow calculations (based on nozzle diameter, layer thickness, and feed rate) even if your gcode has enabled the use of E values with M229 E1 D1.
Example
G2 X50 Y75 I15 J20 E1 F1800
This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
- G2 (working speed clockwise arc/circle move from the current location to)
- X50 (50mm in the X)
- Y75 (75mm in the Y)
- (centered about a point located)
- I15 (15mm further in the X)
- J20 (20mm further in the Y)
- E1 (while extruding)
- F1800 (moving at 1800mm/min)
Example
G2 X50 Y75 I15 J20 E1 S6
This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
- G2 (working speed clockwise arc/circle move from the current location to)
- X50 (50mm in the X)
- Y75 (75mm in the Y)
- (centered about a point located)
- I15 (15mm further in the X)
- J20 (20mm further in the Y)
- E1 (while extruding)
- (using previously established F rate)
- S6 (made up of six sides - resulting in a hexagon with one point at the origin, with all corners inscribed on the circle)
G2.1 Spiral CW Arc1
A G2.1 makes a spiral circular move (only supports full 360 arcs, or Ln * 360). Effective ending X/Y is always the same as the current XY and is not specified (though the actual final position is a function of the number of laps, the pitch, and the reverse code. An end Z can be supplied to have a uniform displacement during the move. The number of full 360 arcs can be specified as well as the pitch (centerline between arcs). An important feature is the "reverse code" to allow the creation of frog toes without having to jump over the frog toe once it's made.
Usage
G2.1 Zn In Jn Pn Ln En Sn Rn Fn
Parameters
Zn is the new Z position to end at (optional and usually not stipulated; will be relative or absolute, depending on current mode) In is the relative distance from the current X position to the center position about which to arc (default 0) Jn is the relative distance from the current Y position to the center position about which to arc (default 0) Pn is the pitch (how close the laps are) in mm (required) Ln is the number of laps to complete (must be a positive integer; you don't need to finish the spiral) En indicates a working or printing move Sn dictates how many segments are used to create the arc (or circle); 0.33333 mm is the default value S values less than 3.0 dictate the length in mm of each segment for this element S values of 3.0 or more dictate how many total segments comprise this element - only allowed on complete circles of 360° Rn is a flag; 0 to spiral in (default), 1 to spiral out Fn is the Feed rate (travel speed) at which to execute this move.
Any values not stipulated remain unchanged. We will print this element with our native Hyrel flow calculations (based on nozzle diameter, layer thickness, and feed rate) even if your gcode has enabled the use of E values with M229 E1 D1.
Example 1
G2.1 I15 J20 P1.2 E1
This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
- G2.1 (working speed clockwise spiral move from the current location)
- (no change in Z)
- (centered about a point located)
- I15 (15mm further in the X)
- J20 (20mm further in the Y)
- (complete all laps)
- P1.2 (1.2 mm between centers of travel of adjacent laps)
- E1 (while extruding)
- (use default S of 0.33333 mm segments)
- (use default R of 0, spiral in toward center from current location)
- (moving at established G1 F speed)
Example 2
G2.1 Z10 I15 J20 P0.5 L50 E1 S9 R1 F1200
This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
- G2.1 (working speed clockwise spiral move from the current location)
- Z10 (change Z position incrementally during move to end at Z10 (relative or absolute, depending on current mode))
- (centered about a point located)
- I15 (15mm further in the X)
- J20 (20mm further in the Y)
- L50 (complete no more than 50 laps)
- P0.5 (0.5 mm between centers of travel of adjacent laps)
- E1 (while extruding)
- S9 (each 360 degrees composted of a total of 9 segments)
- R1 (spiral out from center to current location)
- F1200 (at a speed of 1200 mm/min)
Example 3
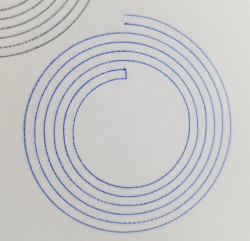
G0 X0 Y25 ; start location for outer spiral G0 Z1 ; go to print layer height G2.1 I25 J0 P4 L3 E1 ; spiral in 3 laps, 4mm pitch G1 X14 E1 ; add connector for the arcs G2.1 I11 J0 P4 L3 E1 R2 ; spiral out 3 laps, 4mm pitch
This gcode generates the following:
G2.2 Spiral CW Arc2
A G2.2 makes a spiral circular move (only supports full 360 arcs, or Ln * 360). Unlike G2.1, G2.2 specifies final X/Y (and Z) location. An end Z can be supplied to have a uniform displacement during the move. The number of full 360 arcs can be specified as well as the pitch (centerline between arcs). Unlike G2.1, G2.2 does not require a reverse code as the direction of spiral is determined by the positional relationship of the current position, final position, and center position.
Usage
G2.2 Xn Yn Zn In Jn Pn Ln En Sn Rn Fn
Parameters
Xn is the new X position to move to Yn is the new Y position to move to Zn is the new Z position to end at (optional and usually not stipulated; will be relative or absolute, depending on current mode) In is the relative distance from the current X position to the center position about which to arc (default 0) Jn is the relative distance from the current Y position to the center position about which to arc (default 0) Pn is the pitch (how close the laps are) in mm (optional) Ln is the number of laps (or paths) to complete (you don't need to finish the spiral) Note, if P and L values conflict, L will be modified to match what P will allow; at least one must be specified En indicates a working or printing move Sn dictates how many segments are used to create the arc (or circle); 0.33333 mm is the default value S values less than 3.0 dictate the length in mm of each segment for this element S values of 3.0 or more dictate how many total segments comprise this element - only allowed on complete circles of 360° Fn is the Feed rate (travel speed) at which to execute this move.
Any values not stipulated remain unchanged. We will print this element with our native Hyrel flow calculations (based on nozzle diameter, layer thickness, and feed rate) even if your gcode has enabled the use of E values with M229 E1 D1.
Example 1
G2.2 I15 J20 P1 E1
This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
- G2.2 (working speed clockwise spiral move from the current location)
- (no change in Z)
- (centered about a point located)
- I15 (15mm further in the X)
- J20 (20mm further in the Y)
- P2 (1mm between centers of travel of adjacent laps)
- (complete all laps)
- E1 (while extruding)
- (use default S of 0.33333 mm segments)
- (moving at established G1 F speed)
Example 2
G2.2 Z10 I15 J20 P2 L50 E1 S9 F1200
This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
- G2.2 (working speed clockwise spiral move from the current location)
- Z10 (change Z position incrementally during move to end at Z10 (relative or absolute, depending on current mode))
- (centered about a point located)
- I15 (15mm further in the X)
- J20 (20mm further in the Y)
- P2 (2mm between centers of travel of adjacent laps)
- L50 (complete no more than 50 laps)
- E1 (while extruding)
- S9 (each 360 degrees composted of a total of 9 segments)
- F1200 (at a speed of 1200 mm/min)
Example 3
G0 X0 Y25 ; start location for outer spiral G0 Z1 ; go to print layer height G2.2 X12 I25 P4 E1 ; spiral in 3 laps, 4mm pitch G1 X14 E1 ; add connector to next spiral G2.2 X2 I11 P4 E1 ; spiral out 3 laps, 4mm pitch
This gcode also generates the following:
G2.3 3-Space CW Arc
A G2.3 move specifies a clockwise arc (or complete circle(s) from the current position to position (X,Y,Z)curr following a circular arc about the center point (Xcurr+I, Ycurr+J, Zcurr+K). Unlike G2, G2.1 and G2.2, G2.3 is not bound to the X/Y plane. The number of full 360 arcs can be specified as well as the pitch (centerline between arcs). Usage
G2.3 Xn Yn Zn An Bn In Jn Kn Un Vn Wn Dn Pn En Sn Fn
Note: If we are in G16 mode, Un, Vn, Wn define the vector normal to the work plane. If we are in G17 (X/Y plane) or G18 (X/Z plane) or G19 (Y/Z plane) mode, these are ignored.
Parameters
Xn is the new X position to end at Yn is the new Y position to end at Zn is the new Z position to end at An is the new A position to end at (4th axis) Bn is the new B position to end at (5th axis) In is the relative distance from the current X position to the center position about which to arc (default 0) Jn is the relative distance from the current Y position to the center position about which to arc (default 0) Kn is the relative distance from the current Z position to the center position about which to arc (default 0) Un is the X component of a vector normal to the working plane (default 0) Vn is the Y component of a vector normal to the working plane (default 0) Wn is the Z component of a vector normal to the working plane (default 0) Dn is the overall displacement normal to the working plane for this element Pn is the pitch (how close the laps are normal to the working plane) in mm (default 0; one path, no incremental displacement) En indicates a working or printing move Sn dictates how many segments are used to create the arc (or circle); 0.33333 mm is the default value S values less than 3.0 dictate the length in mm of each segment for this element S values of 3.0 or more dictate how many total segments comprise this element - only allowed on complete circles of 360° Fn is the Feed rate (travel speed) at which to execute this move.
Any values not stipulated remain unchanged. We will print this element with our native Hyrel flow calculations (based on nozzle diameter, layer thickness, and feed rate) even if your gcode has enabled the use of E values with M229 E1 D1.
G3 Counterclockwise Arc
Please refer to G2, above, for details. All options are identical, with the exception of direction (counterclockwise).
G3.1 Spiral CCW Arc1
Please refer to G2.1, above, for details. All options are identical, with the exception of direction (counterclockwise).
G3.2 Spiral CCW Arc2
Please refer to G2.2, above, for details. All options are identical, with the exception of direction (counterclockwise).
G3.3 3-Space CCW Arc
Please refer to G2.3, above, for details. All options are identical, with the exception of direction (counterclockwise).
G4 Timed Pause
G4 is a pause for a set number of seconds (S) or milliseconds (P).
Usage
G4 Sn Pn
Parameters
Sn is the number of Seconds to pause Pn is the number of Milliseconds to pause
You may use S or P, or if you use both, the total value will be the pause duration.
Example
G4 S0.5
This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
- G4 (Timed pause)
- S0.5 (0.5 seconds)
Example
G4 P500
This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
- G4 (Timed pause)
- P500 (500 milliseconds)
G16 Arc Plane: Any
G16 permits free-form designation of points in space, without limiting them to an axial plane.
G16 through G19 only apply to G2.x and G3.x commands, and define the plane on which the element will be created.
Usage
G16
Parameters
N/A
Example
G16
This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
- G16 (allow element in any orientation)
G17 Arc Plane: XY
G17 restricts this element to the X/Y plane.
G16 through G19 only apply to G2.x and G3.x commands, and define the plane on which the element will be created.
Usage
G17
Parameters
N/A
Example
G17
This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
- G17 (restrict element to X/Y plane)
G18 Arc Plane: XZ
G18 restricts this element to the X/Z plane.
G16 through G19 only apply to G2.x and G3.x commands, and define the plane on which the element will be created.
Usage
G18
Parameters
N/A
Example
G18
This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
- G18 (restrict element to X/Z plane)
G19 Arc Plane: YZ
G19 restricts this element to the Y/Z plane.
G16 through G19 only apply to G2.x and G3.x commands, and define the plane on which the element will be created.
Usage
G19
Parameters
N/A
Example
G19
This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
- G19 (restrict element to Y/Z plane)
M0 Stop Until Resume
M0 is a stop until resume command; text listed after a semicolon will be displayed, and clicking the Play button (which replaces the Pause button) will cause the job to resume. Note that all lines will be truncated at 100 characters.
- ; All text following the ; will be echoed to the print mask (Control Tab).
Additionally, an M0 command can also take the following parameters, and so will pause and then:
Usage
M0 [ SAY | PIC | VID | SEND | BEEP | SHELL ]
Parameters
SAY sample message - the computer will use built-in text-to-speech to echo the message over the speaker(s) PIC C:\sample.jpg - the computer will display the image at the specified location VID C:\sample.mp4 - the computer will play the video at the specified location SEND sample message - the computer will send the message to the Aux port if connected BEEP - the computer will sound a beep SHELL C:\program.exe - the computer will execute the file at the specified location
Note that multiple options can be combined.
Example
M0
This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
- M0 (Pause until Resume)
Example
M0 ; SAY Hello Wilbur ; PIC C:\mr_ed.png
This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
- M0 (Pause until Resume)
- SAY Hello Wilbur (Announce Text: Hello Wilbur)
- PIC C:\mr_ed.png (Display Image: C:\mr_ed.png)
M203 Set G0 Speed
M203 will redesignate the rate at which G0 movements are executed. If undeclared, the values stored in Repetrel for your equipment will be used. These can be changed under Settings > Printer, on the Printer tab. The values set on your unit are set based on testing; exceed them at your own risk.
Usage
M203 Xn Yn Zn An Bn
Parameters
Xn is the new speed in the X axis for G0 moves Yn is the new speed in the Y axis for G0 moves Zn is the new speed in the Z axis for G0 moves An is the new speed in the A axis for G0 moves Bn is the new speed in the B axis for G0 moves
Example
M203 Y2000
This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
- M203 (Set G0 Speed)
- (X remains unchanged)
- Y2000 (Y axis: 2000mm/min)
- (Z remains unchanged)
- (A remains unchanged)
- (B remains unchanged)
Controlling Temperature
| Controlling Temperature | ||
|---|---|---|
| Code | Supported | Brief Description |
| M104 | Yes | Set Temp (Head) |
| M106 | Yes | Set Cooling / Etc. |
| M107 | Yes | Stop Cooling / Etc. |
| M109 | Yes | Wait for Temp (Head) |
| M116 | v5+ | Pause for All Temps |
| M140 | Yes | Set Temp (Bed) |
| M141 | Yes | Set Temp (Chamber) |
| M190 | Yes | Wait for Temp (Bed) |
| M191 | Yes | Wait for Temp (Chamber) |
What's Hotbed 2 and Chamber 2? Well, our Hydra models have room to have a second hotbed, which could be a smaller, higher temperature hotbed, or a sub-ambient chilled bed, or even a High Resolution hotbed. And we've talked about having a smaller chamber inside the primary chamber, to bring the air around the print (but not the head) to much higher temperatures; call for details.
M104 Set Temp (Head)
M104 sets the extruder temperature but does not pause the printer.
Note that the actual T# values can be found on T_v4 or T_v5, depending on which version you are running.
Usage
M104 Sn T#
Parameters
Sn is the new set temperature in °C T# is the tool assignment for this temperature command
Example
M104 T# S75
This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
- M104 (Set Cooling/LEDs)
- T# (target head)
- S75 (to 75°C)
M106 Set Cooling / Etc.
M106 sets the cooling fan (or crosslinking LEDs) speed (or intensity). This also turns on the Quiet Storm fan.
Usage
M106 Cn
or
M106 T# Sn
or
M106 T# Pn
Parameters
T# is the target head Sn is the percent of duty cycle for the cooling fan (or LEDs); default: 100 Cn is the range (0-100 or 0-255) that we will use; if unspecified, the default is C100 (use C255 to be compatible with most slicers) Pn is the percent of duty cycle for the cooling fan (or LEDs) to come on only during extrusion moves
Example
M106 C255
This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
- M106 (Set Cooling/LEDs)
- (on all tools)
- (no speed)
- C255 (of range 0-255)
Note, with this command, all following M106 commands for the rest of this print job will be based on this range (unless specified with a new C value).
Example
M106 T# S50
This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
- M106 (Set Cooling/LEDs)
- T# (target head)
- S50 (target value of 50)
- (previously defined (or default 0-100) range)
Example
M106 T# P100
This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
- M106 (Set Cooling/LEDs)
- T# (target head)
- P100 (during extrusion moves at 100% duty cycle
But Davo, I want to cure a certain spot for 10 seconds with every layer change; how do I do this?
Easy. Edit your slicer recipe to add the following code after layer changes (edit as needed for duration, intensity, or position):
;---- BEGIN COD CODE G91 ; relative moves G0 Z5 ; drop bed G90 ; absolute moves G0 X130 Y110 ; move into position M106 S100 T# ; turn on T# UV at 100% G1 X140 Y110 F100 ; move 10 mm in the X at 100 mm/min G1 X140 Y120 F100 ; move 10 mm in the Y at 100 mm/min G1 X130 Y120 F100 ; move -10 mm in the X at 100 mm/min G1 X130 Y110 F100 ; move -10 mm in the Y at 100 mm/min M106 S0 T# ; turn off T# UV (set it to 0%) ;--- END COD GCODE
These commands are decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
- G91 (Use relative moves)
- G0 (Non-working move)
- Z5 (+5 mm in the Z)
- G90 (Use absolute moves)
- G0 (Non-working move)
- X130 (To position X130)
- Y110 (To position Y110)
- M106 (Set Aux (UV))
- S100 (100% duty)
- T# (On target head)
- G1 (Working (printing) move)
- X140 (To position X140)
- Y110 (To position Y110
- F100 (At 100 mm/min)
- G1 (Working (printing) move)
- X140 (To position X140)
- Y120 (To position Y120
- F100 (At 100 mm/min)
- G1 (Working (printing) move)
- X130 (To position X130)
- Y120 (To position Y120
- F100 (At 100 mm/min)
- G1 (Working (printing) move)
- X130 (To position X130)
- Y110 (To position Y110
- F100 (At 100 mm/min)
- M106 (Set Aux (UV))
- S0 (0% duty)
- T# (On target head)
M107 Stop Cooling / Etc.
M107 turns off the cooling fan (or crosslinking LEDs); this is essentially the same as an M106 S0 (setting it to 0 percent). This will also turn off the Quiet Storm fan.
Usage
M107 T#
Parameters
T# (target head)
Example
M107 T#
This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
- M107 (Set Cooling/LEDs to 0%)
- T# (target head)
M109 Wait for Temp (Head)
M109 waits for the extruder to reach temperature, with an option to also set the temperature. Remember, we have both heated and chilled (sub-ambient) heads as options.
Note that the actual T# values can be found on T_v4 or T_v5, depending on which version you are running.
Usage
M109 T# Sn Hn Cn Ln Un Rn W0
Please use EITHER (H and/or C) OR (L and/or U) OR (R) with your M109 command.
Note, this will FAIL (non-fatally) if you address a virtual group address; be sure to use an actual physical address.
Parameters
T# is the target head
Sn (optional) is the new set temperature in °C; if omitted, no new target temperature is set
Hn if present, is the low-end (or "heat up to") absolute temperature after which we stop pausing
Cn if present, is the high-end (or "cool down to") absolute temperature after which we stop pausing
Ln if present, is the lower-end relative temperature difference from set temp after which we stop pausing
Un if present, is the upper-end relative temperature difference from set temp after which we stop pausing
Rn if present, is how close the relative temperature needs to be to the set temp to end the pause
W0 if present, will set the temp and advance to the next line without pause, but upon executing M116, will pause until temp is reached
Think of Sn as the target temperature, but once the target is between Cn (or Ln) and Hn (or Un), the pause is over (but the Sn is still the set temp to reach. You can use Hn or Ln, but not both. You can use Cn or Un, but not both.
Example 1
M109 T# S240
This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
- M109 (wait for temp)
- T# (target head)
- S240 (and set temp to 240°C)
Example 2
M109 T# S240 R5
This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
- M109 (wait for temp)
- T# (target head)
- S240 (and set temp to 240°C)
- R5 (but end the wait once the target's temperature is within 5°C of the set point)
Example 3
M109 T# S240 H230
This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
- M109 (wait for temp)
- T# (target head)
- S240 (and set temp to 240°C)
- H230 (but end the wait once the target's temperature reaches 230°C)
Example 4
M109 T# S240 L10 U5
This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
- M109 (wait for temp)
- T# (target head)
- S240 (and set temp to 240°C)
- L10 (but end the wait once the target's temperature reaches 10°C below the set point)
- U5 (or end the wait once the target's temperature reaches 5°C above the set point)
Note: this wait ends when the target's temperature is anywhere between 230°C and 245°C
Example 5
M109 T# S0 R5
This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
- M109 (wait for temp)
- T# (target head)
- S0 (to 0°C)
- R5 (but end the wait once the target's temperature is +/-5°C of the set temperature)
Example 6
M109 R10
- M109 (wait for temp)
- (no T# - use head with current focus)
- R10 (to get +/-10°C of set temperature)
Example 7
M109 T# S240 W0 This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
M116 Wait for Temps (v5+)
M140 Set Temp (Bed)M140 sets the bed temperature (without waiting for the new temperature to be reached). Usage M140 Sn T# Parameters Sn is the new set temperature in °C T# is the target bed (default is the primary bed) Example M140 S75 This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
M141 Set Temp (Chamber)M141 sets the chamber temperature (without waiting for the new temperature to be reached). Usage M141 Sn T# Parameters Sn is the new set temperature in °C T# is the target chamber (default is the primary chamber) Example M141 S75 This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
M190 Wait for Temp (Bed)M190 waits for the bed to reach temperature, with an option to also set the temperature. Remember, we have both heated and chilled (sub-ambient) beds as options. Usage M190 T# Sn Hn Cn Ln Un Rn Please use EITHER (H and/or C) OR (L and/or U) OR (R) with your M190 command. Note, this will FAIL (non-fatally) if you address a virtual group address; be sure to use an actual physical address. Parameters T# is the target bed (default is the primary (or only) bed) Sn (optional) is the new set temperature in °C; if omitted, no new target temperature is set Hn if present, is the low-end (or "heat up to") absolute temperature after which we stop pausing Cn if present, is the high-end (or "cool down to") absolute temperature after which we stop pausing Ln if present, is the lower-end relative temperature difference from set temp after which we stop pausing Un if present, is the upper-end relative temperature difference from set temp after which we stop pausing Rn if present, is how close the relative temperature needs to be to the set temp to end the pause Think of Sn as the target temperature, but once the target is between Cn (or Ln) and Hn (or Un), the pause is over (but the Sn is still the set temp to reach. You can use Hn or Ln, but not both. You can use Cn or Un, but not both. Example 1 M190 T# S240 This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
Example 2 M190 T# S240 R5 This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
Example 3 M190 T# S240 H230 This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
Example 4 M190 T# S240 L10 U5 This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
Note: this wait ends when the target's temperature is anywhere between 230°C and 245°C Example 5 M190 T# S0 R5 This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
Example 6 M190 R10
M191 Wait for Temp (Chamber)M191 waits for the chamber to reach temperature, with an option to also set the temperature. Remember, we have both heated and chilled (sub-ambient) chambers as options. Usage M191 T# Sn Hn Cn Ln Un Rn Please use EITHER (H and/or C) OR (L and/or U) OR (R) with your M191 command. Note, this will FAIL (non-fatally) if you address a virtual group address; be sure to use an actual physical address. Parameters T# is the target chamber (default is the primary (or only) chamber) Sn (optional) is the new set temperature in °C; if omitted, no new target temperature is set Hn if present, is the low-end (or "heat up to") absolute temperature after which we stop pausing Cn if present, is the high-end (or "cool down to") absolute temperature after which we stop pausing Ln if present, is the lower-end relative temperature difference from set temp after which we stop pausing Un if present, is the upper-end relative temperature difference from set temp after which we stop pausing Rn if present, is how close the relative temperature needs to be to the set temp to end the pause Think of Sn as the target temperature, but once the target is between Cn (or Ln) and Hn (or Un), the pause is over (but the Sn is still the set temp to reach. You can use Hn or Ln, but not both. You can use Cn or Un, but not both. Example 1 M191 T# S240 This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
Example 2 M191 T# S240 R5 This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
Example 3 M191 T# S240 H230 This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
Example 4 M191 T# S240 L10 U5 This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
Note: this wait ends when the target's temperature is anywhere between 230°C and 245°C Example 5 M191 T# S0 R5 This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
Example 6 M191 R10
Controlling Material Flow
You can specify flow rate variables in your gcode; we do not do this by default, but take these values from the head itself. Any values you stipulate in your gcode will supersede the values stored on the head. With our recipes the slicing program generates gcode which dictates temperature and movement commands and indicates which moves should dispense material (a G1 move with an E value). However, we have two different ways to control flow.
When a head is loaded, it sends this flow data (how to calculate flow, as well as how much to prime and unprime (advance and retract) material when transitioning between printing and non-printing moves - and even how many primes or unprimes to do in conjunction with a tool change. In this way, the very same gcode (with temperature changes) can be used with any material, provided you are using the same physical parameters that the model was sliced for.
G10 UNUSED1G10 is not recognized by Repetrel. On some other printers, this will set tool offsets; we do this via M6. On some other printers, this will do a retract; we do this via M721.
G11 UNUSEDG11 is not recognized by Repetrel. On some other printers, this will do an advance or unretract; we do this via M722.
M82 Absolute E-ValuesM82 stipulates that henceforth, the extrusion positioning (E values) will be calculated from the original (0) point. Note, this only works on v4 and later, when E values are enabled via M229. Usage M82 Parameters N/A Example M82 This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
M83 Relative E-ValuesM83 stipulates that henceforth, the extrusion positioning (E values) will be calculated from the relative (last used) point. Note, this only works on v4 and later, when E values are enabled via M229. Usage M83 Parameters N/A Example M83 This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
M221 Set Flow RateM221 sends information to the printer about material flow. Note, our default mode is volumetric calculations; if you need to slice with linear calculations, multiply your Pn by approximately 2.4 (you can do the math). Usage M221 Pn Sn Wn Zn T# Parameters Pn is the number of pulses on the motor to dispense 1 μl (for volumetric) or 1 mm (for linear) of material; Sn is the direct flow multiplier (to allow for undersized or oversized stock; Wn is the width of the cross section of the volume to fill; Zn is the height (layer thickness) of the cross section of the volume to fill; and T# is the tool (head) to which these values will be applied. Example M221 S1.0 T# P77 W0.5 Z0.3 This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
M229 Use E ValuesStarting with version 4, Hyrel will begin to enable the use of E-values in your gcode. Variable extrusion width and support/infill thickness slicers, rejoice! Note, calculations are done for every single move individually. Usage M229 En Dn Sn Parameters En can be 0 (native flow calculation) or 1 (use E values) Dn how directed to head; see below D0 on head controller directly; constant flow, not adjusted for motion acceleration/deceleration D1 on motion controller, sent to head via CANBUS and adjusted for motion acceleration/deceleration D2 on motion controller, sent to head via C axis step pin and adjusted for motion acceleration/deceleration D3 on motion controller, sent to head via CANBUS and C axis and adjusted for motion acceleration/deceleration Sn sets a threshold in seconds; isolated non-printing moves below this threshold will not trigger unprime/prime actions Note: E1 D0 is an illegal combination. Example 1 M229 E1 D1 This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
Above is the default way to enable E values. Example 2 M229 E0 D0 This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
Above is the default way to ignore E values, and is how v3 and earlier releases work. Example 3 M229 E0 D1 This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
Example 4 M229 E0 D0 S0.02 This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
M721 Set Unprime ValuesM721 sends information to the printer about how much material to unprime when a transition from printing move to non-printing move is detected. Usage M721 Sn En Pn T# In Parameters Sn is the speed at which unprime moves should be executed; this is normally 10,000 En is the number of pulses on the feed (extrusion) motor to execute; this varies greatly among materials Pn is the number of milliseconds relative to the end of the move to begin the unprime (retract) action; a negative number initiates this before the end of the move T# is the target head In is the flag for executing an Immediate action; so M721 I1 would execute an unprime with the previously specified values at that point in the gcode. Example 1 M721 S10000 E100 P-15 T# This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
Example 2 M721 T# I1 This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
M722 Set Prime ValuesM722 sends information to the printer about how much material to prime (advance) when a transition from non-printing move to printing move is detected. This is done primarily to compensate for an earlier unprime (retract), to prep the head to be ready to dispense. Usage M722 Sn En Pn T# In Parameters Sn is the speed at which unprime moves should be executed; this is normally 10,000 En is the number of pulses on the feed (extrusion) motor to execute; this varies greatly among materials Pn is the number of milliseconds to dwell relative to the start of the move to allow for the prime (advance) action T# is the target head In is the flag for executing an Immediate action; so M722 I1 would execute a prime with the previously specified values at that point in the gcode. Example M722 S10000 E100 P-15 T# This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
Example M722 T# I1 This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
M723 Set Manual FlowM723 tells the designated extruder(s) to advance material for the specified number of pulses (on the motor) at the specified rate, regardless of any X/Y/Z movement. It is normally used only during manual operation, not during gcode execution. It can be used after moving to a location to dispense a set amount of material (like depositing material into reservoirs). M723 is also used to activate and set speed on the stirring apparatus on the DMH dynamic mixing head.
M723 Sn En T# Parameters Sn is the speed at which the motor should advance, in pulses per second (default: 500); En is the number of pulses on the feed (extrusion) motor to execute (default: 65535); T# is the target head Example M723 S500 E65535 T# This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
M728 Set Motor Current BoostM728 will set the motor current boost; default is 0. Usage M728 Sn T# Parameters Sn is the new set temperature in °C T# is the target head (or device) Example M728 T# S0 This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
M756 Set Height for FlowM756 will overwrite the Z value from the M221 command, allowing you to calculate flow for thinner or thicker layers. We declare M756 at the beginning of every layer; normally, they are all the same (unless you sliced for varying layer thicknesses). Note: this command is ignored if you are using M229 E1 D1 to enable use of E values. Usage M756 Sn Parameters Sn is the layer thickness in mm for flow calculations Example M756 S0.125 This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
Controlling Position and Offsets
The following commands define if new positioning data is defined in inches (G20) or mm (G21); or from the origin (G90) or from the present location (G91). They also stipulate the offsets from one head to another (M6), and how to invoke that offset (T). G10 UNUSED2G10 is not recognized by Repetrel. On some other printers, this will set tool offsets; we do this via M6. On some other printers, this will do a retract; we do this via M721. G20 Set Units to InchesG20 declares that henceforth, measurements will be given in inches. Working with G20 is experimental and unsupported on Hyrel equipment. Use at your own risk. Usage G20 Parameters N/A Example G20 This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
G21 Set Units to MillimetersG21 declares that henceforth, measurements will be given in mm. Usage G21 Parameters N/A Example G21 This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
G28 Send X, Y to Physical HomeG28 sends the X and/or Y axes to the sensor-defined physical home position, regardless of logically set 0,0, then pop-off and re-acquire the sensor threshold at a slower rate. This pop-off and re-acquire was implemented during v3. After homing, a G28 also resets current offsets to 0 - including any may have been set with a G92 or an H (as defined in an M660 and invoked on a G1), performs a G53, and applies a head offset of 0 mm (as in an M6 O0). Any axis not homed will have its position remain unchanged. We do not support intermediate positioning during homing. Usage G28 Xn Yn Zn An Bn I1 Parameters X0 ensures that the X axis is homed Y0 ensures that the Y axis is homed Z0 ensures that the Z axis is homed A0 ensures that the A axis is homed B0 ensures that the B axis is homed Example G28 X0 Y0 This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
G53 Clear OffsetsG53 sets the fixture offsets to (0,0,0,0,0). This takes no arguments or variables. It does not clear stored offset values. Usage G53 Parameters N/A Example G53 This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
G54 - G59 - Set OffsetsG54, G55, G56, G57, G58, and G59 will each store and invoke fixture offsets in the X, Y, Z, A, and/or B axes for all subsequent moves. Any values not invoked will remain with their previous value (0 unless earlier specified otherwise). These offsets apply to all positioning until a new offset is applied, or a G53 is used to clear all offsets. Note that this differs from an M6, where the offsets are only applied to a SINGLE tool position. These offsets are cumulative with M6 values. Usage G54 (... G59) Xn Yn Zn An Bn Parameters Xn is the offset in mm in the X axis Yn is the offset in mm in the Y axis Zn is the offset in mm in the Z axis An is the offset in mm in the A axis Bn is the offset in mm in the B axis Example G54 X30 Y-20 This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
Example G55 This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
G90 Absolute PositioningG90 stipulates that henceforth, the positioning will be calculated from the origin (0,0 point). Usage G90 Parameters N/A Example G90 This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
G91 Relatative PositioningG91 stipulates that henceforth, the positioning will be calculated relative to the starting position. Usage G91 Parameters N/A Example G91 This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
G92 Reset Coordinate OffsetsG92 resets the current position to the specified coordinates for all axes enumerated. Usage G92 Xn Yn Zn An Bn En Parameters Xn is the new value for the current X position Yn is the new value for the current Y position Zn is the new value for the current Z position An is the new value for the current A position Bn is the new value for the current B position En is the new value for the current E position Example G92 X0 Y50 This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
Example G92 E0 This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
G93 Clear Coordinate OffsetsG93 clears ALL offsets implemented via G92 command. Usage G93 Parameters N/A Example G93 This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
M6 Declare Head OffsetsM6 declares that a particular head holds a set of X, Y, and/or Z offsets, which will be invoked during a T (tool change) command. Repetrel reads this data from the heads, and sends it to the printer before the gcode file is loaded. Usage M6 T# On Xn Yn Zn An Bn Dn In Kn Parameters T# is the Tool position for which these offsets are being set On is the Offset position where these are being stored Xn is the offset in the X axis Yn is the offset in the Y axis Zn is the offset in the Z axis An is the offset in the A axis Bn is the offset in the B axis Dn is the current tool diameter (used with pocket commands) In non-persistent; can be default 0 (store values but do not move these distances) or 1 (store values and move these distances) Kn persistent setting; can be default 0 (use I value) or 1 (ignore I1 and always act with I0) Example M6 T# O1 X20 Y-30 Z40 This happens (for every head loaded) when you click print, and the head values are sent to the Motion Controller. This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
Example M6 T# O1 X20 Y-30 Z40 I1 This happens when you execute a tool change with T#, and so it triggers the move (I1) to properly position the next head. This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
Example M6 K1 You might include this in your header to change behavior during tool changes. This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
Note that this differs from a G54-G59, where the offsets are applied to EVERY tool position.
M660 Assign Tool Height OffsetUsed with the High Resolution Engine (and other units which home away from O, like a CNC), an M660 declares that a particular head, when called upon, should print at the gcode-based Z position MODIFIED by this offset, since on these units, the Z-Zero is often BELOW the print surface. By default, this is ONLY used on the EHR (Engine, High Resolution) NOTE: You MUST have a G28 Z0 in your header to run this M660 on the EHR. Usage M660 Hn Zn (followed by) G1 Xn Yn Zn Fn Hn (see #G1_Working_Move for other details Parameters H is the head offset registern for which these offsets are being set; Z is the offset in the Z axis in mm. Example 1 M660 H2 Z28.2 ; (specified before any moves) (followed by) G1 X50 Y75 F4800 H2 ; (specified on the first G1 move) This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
To be clear, this requires editing two lines of code: In your gcode, you will enter the M660 just before the first layer code. Example: Example 2 Before editing: G1 Z0.275 F360 ; move to next layer (0) (followed by) G1 X50 Y75 F4800 After editing: G1 Z0.275 F360 H2 ; move to next layer (0) and invoke head Z offset for this tool (followed by) G1 X50 Y75 F4800 H2
M702 - M704 Cloning HeadsClone, slave, or parallel printing, is when multiple heads make the exact same print at the same time. Usage of these commands with version 4 and earlier is explained on T_v4. Usage of these commands with version 5 and later is explained on T_v5.
T Tool ChangeT executes a tool change, invoking the parameters specified in the M6 sent from Repetrel to the printer at the job start. Do not confuse a T command with a T variable. See the first entry on this page for details.
Controlling Lasers and UV Pens
M620 Enable DeviceM620 enables the device. Usage M620 T# En An Parameters T# is the tool position En can be the default 0 (disable) or 1 (enable) An is the duration in seconds after shut-off that the cooling remains active; default is 30 (but this will not override temperature safety measures) Example M620 T# E1 This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
M621 Set Laser PowerM621 sets the power for the LASER (not other heads). Usage M621 Dn Pn Parameters Pn is the power, in a value between 0 (min) and 100 (max). Dn is the initial power (similar to a prime) to penetrate material (optional; uses Pn if unspecified) Note: No tool is specified; this will happen on the laser already enabled with M620. Example M621 P40 This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
M623 Duration EmitM623 sets the power for the laser or UV pen, and takes the following parameters: Usage M623 Dn Pn Parameters Dn is the duration, in miliseconds (only used for static exposures, not during moves) Pn is the power, in a value between 0 (min) and 100 (max). Note: Dn max for UV pens is 60,000 (1 minute); Dn max for other devices 1,000 (1 second); Here are examples: M623 P80 D500 This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
M623 P80 D10000 This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
Laser ExamplesA sample of code for lasering will look like this: G0 X100 Y100 F1000 ; move to start location at 1000 mm/min M620 T# E1 ; enable target device M621 P100 ; set light emission in vector mode (slot 3) to full power (100%) T# ; toolchange to target head G1 X120 Y100 E1 ; emitting (printing) move 20mm from origin in X axis G1 X120 Y120 E1 ; emitting (printing) move 20mm from origin in Y axis G1 X120 Y130 ; non-emitting move 10mm from origin in Y axis G1 X140 Y130 E1 ; emitting move 20mm from origin in X axis ... (the rest of your lasering job) M620 T# E0 ; disable target device <= should be before M30 command UV Pen ExamplesA sample of code for UV Curing will look like this: G0 X100 Y100 F1000 ; move to start location at 1000 mm/min M620 T# E1 ; enable target device M621 P100 ; set light emission in vector mode (slot 3) to full power (100%) T# ; toolchange to target head G1 X120 Y100 E1 ; emitting (printing) move 20mm from origin in X axis G1 X120 Y120 E1 ; emitting (printing) move 20mm from origin in Y axis G1 X120 Y130 ; non-emitting move 10mm from origin in Y axis G1 X140 Y130 E1 ; emitting move 20mm from origin in X axis ... (the rest of your curing job) M620 T# E0 ; disable target device <= should be before M30 command For more complex examples, see the UV_and_Clench page.
Controlling Spindles and Lathes
Machining and Spindle Tool commands. Note, we recommend using SimplyCAM. You can review the 5-axis gcode we used for this video from here. M3 Turn On Spindle (CW)M3 tells the printer to activate (start) the spindle motor in the clockwise direction on the current head (if it has one), using the value set on the head for RPM. Note: S0 is the same as turning it off. Note: DO NOT CHANGE DIRECTION while the spindle is in motion. Usage M3 T# Sn Fn Parameters T# - target head Sn - power (0-100%) Fn - optional; PWM in Hz (defaults on heads should be fine for most uses) Example M3 T# S75 This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
M4 Turn On Spindle (CCW)Please refer to M3, above, for details. All options are identical, with the exception of direction (counterclockwise).
M5 Turn Off SpindleM5 tells the printer to deactivate (stop) the spindle motor on the current head (if it has one). M5 has the same effect as M3 S0 or M4 S0. Usage M5 T# Parameters T# - target head Example M5 T# This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
M253 Turn On Lathe (CW)M253 tells the printer to activate (start) the lathe motor in the clockwise direction (if it has one), using the value set with M92 for RPM. Only available on Hydra 16A models. Note: S0 is the same as turning it off. Usage M253 Sn Parameters Sn - speed in units per minute (default: RPM if set with M92 as steps per revolution) Example M253 S75 This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
M254 Turn On Lathe (CCW)Please refer to M253, above, for details. All options are identical, with the exception of direction (counterclockwise).
M255 Turn Off LatheM255 tells the printer to deactivate (stop) the lathe motor (if it has one). M255 has the same effect as G253 S0 or G254 S0. Usage M255 Parameters N/A Example M255 This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
G81 Peck DrillingG81 tells the printer to move to a start position in X/Y and then in Z, and to make (if needed) repeated descents and retracts. This is used to make holes, especially deep holes. Note that the spindle tool is turned on with an M3 or M4 before this command, and turned off with an M5 after all work is done. Usage G81 T# Xn Yn In Pn Qn Zn Fn Parameters T# - target head Xn - X position Yn - Y position In - initial Z position Pn - peck downward this many mm during each cycle Qn - retract upward this many mm after each cycle (to clear debris) Zn - maximum pecking depth Fn - Z working speed in mm/min Example G81 T# X100 Y75 I3 P3 Q-2 Z-7.5 F200 NOTE that an M660 offset must be set and applied BEFORE THIS COMMAND to allow for tool length. This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
Reporting and Diagnostics
The following commands help with reporting and diagnostics. Most users never need them, but here are the basics. More advanced/detailed reporting is available. M701 Set Head ReportingM701 tells heads how often to send head-specific information to the Motion Controller and on to Repetrel (and pass along to a text file if enabled via M719). Usage M701 T# Pn Parameters T# - target head Pn - period in seconds between entries (default 1) Example M701 P12 This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
M718 Stop Logging to FileM718 tells Repetrel to stop any logging of data to text file that may have been enabled with M719. Usage M718 Parameters N/A Example M718 This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
M719 Start Logging to FileM719 tells the Motion Controller what system-wide information to report back to Repetrel, and also tells Repetrel to begin logging these details to a text file. Usage M719 Pn Sn M719 Pn Xn Yn Zn An Bn Vn En Ln Parameters Pn - period in seconds between entries Sn - can be default 0 (see options below) or 1 (report ALL data) Xn - report X position with each entry Yn - report Y position with each entry Zn - report Z position with each entry An - report A position with each entry Bn - report B position with each entry Vn - report velocity with each entry En - report flow rate with each entry Ln - report gcode line number with each entry Note: these values are persistent, and if previously enabled, will still be enabled unless disabled with a 0 parameter. Example 1 M719 P10 S1 This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
Example 2 M719 P.1 Xn Yn Zn Ln
M670 Enable Gantry / Y-arm LightM670 sets the intensity of the Y-arm LEDs. Usage M670 Sn Pn Parameters Sn is the (percent of duty cycle, 0-100) for the LEDs Pn is the period (on-off interval - default is 1 second) Example 1 M670 S50 P1 This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
This would turn the Y-arm light on for 50% of 1 second, then off for 50% of 1 second - or on for 0.5 seconds, off for 0.5 seconds. Example 2 M670 S25 P4 This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
This would turn the Y-arm light on for 25% of 4 second, then off for 75% of 4 seconds - or on for 1 second, off for 3 seconds.
M672 Set Gantry / Y-arm StateM672 can be used to have the Gantry / Y-arm light change states to reflect the state of a sensor. For example, you can have it come on when the X axis is homed, or when the Y axis has a fault. Usage M672 Sn Parameters Sn can be (unlisted numbers are unused at present):
0 : Normal on/off
10 : X Home
11 : X Limit1
12 : X Limit2
13 : X Fault
20 : Y Home
21 : Y Limit1
22 : Y Limit2
23 : Y Fault
30 : Z Home
31 : Z Limit1
32 : Z Limit2
33 : Z Fault
40 : A Home
41 : A Limit1
42 : A Limit2
43 : A Fault
50 : B Home
11 : B Limit1
52 : B Limit2
53 : B Fault
60 : C Home
61 : C Limit1
62 : C Limit2
63 : C Fault
Example M672 S This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
M772 Reset All MetricsM772 will reset all internal gathering registers to 0. Usage M772 Sn Parameters Sn 0 is default; S can be...
0 reset all values only
1 also generates a basic printing report
255 also generates all possible reports (helpful for advanced debugging)
Example M772 S1 This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
M773 Generate Basic ReportM773 generates a basic report of printing statistics (including average speed, number of primes, etc.) Note: this report will be more meaningful if you use M772 to reset these counters at the start of a job. Usage M773 Parameters N/A Example M773 This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
Sample Output >IN: 50: ****************************************************************** >IN: 50: ** Begin M773 - print job metrics Report >IN: 50: ****************************************************************** >IN: 50: >IN: 50: Time (s) Dist (m) >IN: 50: -------- -------- >IN: 50: Totals: 0.0 0.000 >IN: 50: >IN: 50: Printing moves: 0.0 0.000 >IN: 50: Non-printing moves 0.0 0.000 >IN: 50: >IN: 50: Accelerating: 0.0 0.000 >IN: 50: Cruising: 0.0 0.000 >IN: 50: Decelerating: 0.0 0.000 >IN: 50: >IN: 50: can e steps issued: 0 >IN: 50: approx filament (PI*d) 0.000 m >IN: 50: approx filament (PIr^2) 0.000 m >IN: 50: unprimes issued: 0 >IN: 50: primes issued: 0 >IN: 50: unprime-primes avoided: 0 >IN: 50: >IN: 50: ****************************************************************** >IN: 50: ** End M773 Report >IN: 50: ******************************************************************
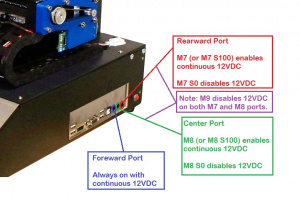
Controlling Aux Devices
M7 Activate Aux 1M7 sends 12VDC to the port associated with "Mist Coolant", which we sometimes call Aux1. With no parameters, it is read as M7 S100 (on continuously). Usage M7 Sn Parameters Sn is the percentage (0-100) for Aux 1 to come on (default is 100) Example 1 M7 S100 This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
Example 2 M7 S25 This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
Example 3 M7 S0 This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
M8 Activate Aux 2M7 sends 12VDC to the port associated with "Flood Coolant", which we sometimes call Aux2. With no parameters, it is read as M8 S100 (on continuously). Usage M8 Sn Parameters Sn is the percentage (0-100) for Aux 2 to come on (default is 100) Example 1 M8 S100 This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
Example 2 M8 S25 This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
Example 3 M8 S0 This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
M9 Deactivate Aux1 & Aux2M9 cuts power to both Aux1 and Aux2. It is equivalent to running M7 S0 and M8 S0. Usage M9 Parameters N/A Example M9 This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
M620 Activate EmitterSee #M620_Enable_Device above.
M670 Activate Gantry / Y-ArmM670 sends 12VDC to the port associated turning on the Gantry (16A) or Y-arm (30M, ESR) lights. Usage M670 Sn Parameters Sn is the percentage (0-100; no default - if no Sn, no change) Example 1 M670 S100 This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
Example 2 M670 S25 This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
Example 3 M670 S0 This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
M671 Activate Danger LightsM671 sends 12VDC to the port associated turning on the X-arm / Danger lights (30M/ESR only). Usage M671 Sn Parameters Sn is the percentage (0-100; no default - if no Sn, no change) Example 1 M671 S100 This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
Example 2 M671 S25 This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
Example 3 M671 S0 This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
M675 Activate Response LEDsM675 sends 12VDC to the port associated turning on the Response LEDs (30M/16A only). Usage M675 Sn Parameters Sn is the percentage (0-100; no default - if no Sn, no change) Example 1 M675 S100 This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
Example 2 M675 S25 This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
Example 3 M675 S0 This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
M676 Activate Recirc. FanM676 sends 12VDC to the port associated turning on the Recirc. Fan (16A only). Usage M676 Sn Parameters Sn is the percentage (0-100; no default - if no Sn, no change) Example 1 M676 S100 This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
Example 2 M676 S25 This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
Example 3 M676 S0 This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
M677 Activate BuzzerM677 sends 12VDC to the port associated turning on the Buzzer (older 30Ms only). Usage M677 Sn Parameters Sn is the percentage (0-100; no default - if no Sn, no change) Example 1 M677 S100 This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
Example 2 M677 S25 This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
Example 3 M677 S0 This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
M678 Activate Laser X-hairM678 sends 12VDC to the port associated turning on the Laser X-hair (16A with CO2 lasers only). Usage M678 Sn Parameters Sn is the percentage (0-100; no default - if no Sn, no change) Example 1 M678 S100 This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
Example 2 M678 S25 This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
Example 3 M678 S0 This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
M679 Activate VacuumM679 sends 12VDC to the port associated turning on the Vacuum (30M/ESR only). Usage M671 Sn Parameters Sn is the percentage (0-100; no default - if no Sn, no change) Example 1 M679 S100 This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
Example 2 M679 S25 This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
Example 3 M679 S0 This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
M684 Activate ExhaustM671 sends 12VDC to the port associated turning on the Exhaust (16A only). Usage M684 Sn Parameters Sn is the percentage (0-100; no default - if no Sn, no change) Example 1 M684 S100 This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
Example 2 M684 S25 This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
Example 3 M684 S0 This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
M685 Set Power on AirM685 sends 12VDC to the port associated turning on the (positive pressure) Air (16A only). Usage M685 Sn Parameters Sn is the percentage (0-100; no default - if no Sn, no change) Example 1 M685 S100 This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
Example 2 M685 S25 This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
Example 3 M685 S0 This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
M689 Activate Ext. HeadM689 sends 12VDC to the port associated turning on the Ext. Head. Usage M689 Sn Parameters Sn is the percentage (0-100; no default - if no Sn, no change) Example 1 M689 S100 This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
Example 2 M689 S25 This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
Example 3 M689 S0 This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
Other Commands
Other commands. M17 Engage MotorsM17 will apply power to all motors (positioning and extruder motors), locking them at their current postion; this prevents the bed and yoke from being pushed manually in the X and Y. Note that an M18 or M84 will disengage motors. Usage M17 Parameters N/A Example M17 This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
M18 Disengage MotorsM18 will cut power to all motors (positioning and extruder motors), unlocking them; this allows the motors to cool down (as they normally lock in place while still), as well as allowing one to manually push the bed and yoke in the X and Y. It also notifies the GUI that motors are disabled. All axes with homes must be rehomed after an M18. Note this is identical to M84 and the opposite of M17. Usage M18 Parameters N/A Example M18 This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
M30 End of ProgramM30 tells the printer that this job is complete. No gocde after an M30 will be executed as part of the previous job. Note M30 also dissolves any cloning setups, changes head index to 0, clears fixture offsets (G53), clears any M229 E-value settings, resets M106 persistent range, resets any printing errors, resets M660 head offsets to 0, resets heads to their stored values, and triggers any queued reports. Usage M30 Parameters N/A Example M30 This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
M84 Disable MotorsM84 invokes an M18. Please see M18 for usage.
M783 Tie Aux to ExtrusionM783 can tie some auxiliary port (like Aux 1) to be powered (at 100%) during a certain head's extrusion. Some users use this so that they can print with an Ultimus head on our equipment. Note: M619 can be used to map which port M783 ties to. Usage M783 T# Parameters T# is the tool to which the designated aux port will be tied Example M783 T# This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
M790 New Layer ActionsM790 will trigger any associated new layer actions, which can include capturing an image from the designated camera. It takes no parameters. M791 Snap ImageM791 will cause the camera selected under the Interface > Camera1 tab, if set to live video, to capture an image and save it to M792 Execute ActionM792 causes Repetrel to perform an action, such as displaying an image or making a warning beep. Usage M792 [ SAY | PIC | VID | SEND | BEEP | SHELL ] Parameters SAY sample message - the computer will use built-in text-to-speech to echo the message over the speaker(s) PIC C:\sample.jpg - the computer will display the image at the specified location VID C:\sample.mp4 - the computer will play the video at the specified location SEND sample message - the computer will send the message to the Aux port if connected BEEP - the computer will sound a beep SHELL C:\program.exe - the computer will execute the file at the specified location Note that multiple options can be combined. Example M792 ; SAY Hello Wilbur ; PIC C:\mr_ed.png This command is decoded and executed by the printer as follows:
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||